Why Do 90% of AI Projects Fail? Complete Guide to Data Preparation for AI

Introduction: The Hidden Truth About AI Projects
You bought an expensive AI tool. Deployed it. And now? It hallucinates. Responds with nonsense. Returns outdated information.
Why? Because you skipped the most important step – data preparation.
According to the Data Trust Report 2025, 41% of organizations admit problems with maintaining consistent data quality, which negatively affects AI implementation. And that's just the tip of the iceberg.
"Bad data = bad AI. It's that simple."
In this article, we'll show you:
- Why data quality is critical for AI success
- 4 main problems with RAG projects (95% fail in production)
- How to properly prepare data for RAG systems
- 5 chunking strategies with concrete examples
- What RAGus.ai is and how it solves the hallucination problem
Main Problems with RAG & Gen AI Projects
95% of RAG projects fail in production. Why? We've identified 4 main causes:

Problem #1: Data Structure
How to upload company data (tens of thousands of unstructured URLs and documents) into a knowledge base in structured format?
- A: Data dumped into the KB without any preprocessing / proper structure
- B: KB cannot return valid information to answer user queries with precision and without hallucinations
- C: Data needs to have high quality and consist of unique information (removing unnecessary boilerplate)
Problem #2: Chunking
In an ideal world, each document or URL's content would sit in its own fit chunk with cleaned and well-structured information.
Reality:
- Vector stores have token limits: 500–4096 tokens per chunk
- Most platforms use naive chunking strategies:
- Divide content by fixed token counts
- Allow around 800-1500 tokens for single chunk
- Text cut in the middle of sentences
- Context lost = retrieval fails
- Fixed token overlap
Problem #3: Metadata
Each chunk should have rich and detailed metadata:
- Origin (document filename / page number, URL link)
- Fields for filtering
- Current chunk summary
- Chunk overlap summary
- Source page summary
Problem #4: Automated Updates
- KB built once, never updated
- AI gives old information
- Or simply hallucinates
💡 Don't want to handle this yourself? As an AI company with 30+ successfully completed projects, we offer turnkey data preparation. From audit to final integration — we take care of everything.
What is RAG and Why is it Key to Accurate AI
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG is a technology that combines searching for relevant information with the generative capabilities of AI models.

Instead of AI answering only from its trained knowledge (which may be outdated), RAG:
- Retrieval: Finds relevant documents in the knowledge base
- Augmentation: Adds found information to the context
- Generation: AI generates a response based on current data
Why RAG Works Better Than Classic LLM
| Aspect | Classic LLM | RAG |
|---|---|---|
| Data freshness | ❌ Outdated (training) | ✅ Current (live data) |
| Source citations | ❌ Cannot verify | ✅ Link to source |
| Hallucinations | ❌ Frequent | ✅ Minimal |
| Accuracy | ~70-80% | 90-99% |
How to Properly Prepare Data for AI
4-Step Data Preparation Process

Step 1: Source Mapping
We go through everything – web, documents, databases, emails, internal systems. We find out what you have and in what condition.Step 2: Cleaning and Unification
Gone with duplicates. Gone with inconsistencies. One source of truth. One structure.Step 3: Enrichment and Splitting
We add metadata, summaries, relationships. We split using optimal strategy. AI then knows where to look.Step 4: Creating Your "Second Brain"
We upload everything into one knowledge base – your central source of truth.💡 Don't want to handle this yourself? We offer professional data preparation turnkey. Experience from 30+ projects.
Chunking Strategies: Complete Guide with Examples
AI doesn't read entire documents. It works with "chunks" – pieces of text. How you split them determines how it will answer.
Bad splitting = bad results.
Example Text for All Strategies
For comparison, we'll use the same text about the Kepler space telescope:
# The Kepler Space Telescope
The Kepler space telescope was a space observatory launched by NASA to discover Earth-size planets orbiting other stars. It was named after astronomer Johannes Kepler.
## Mission Overview
Kepler's sole instrument was a photometer that continually monitored the brightness of approximately 150,000 main sequence stars in a fixed field of view. It looked for periodic dimming, known as transits, caused by planets crossing in front of their host star.
## Major Discoveries
During its nine-year mission, Kepler observed 530,506 stars and confirmed 2,662 planets. A key finding was that 20-50% of stars visible to the naked eye likely have small, rocky planets similar in size to Earth.
## End of Operations
The mission ended in 2018 when the spacecraft ran out of fuel. The telescope was deactivated, but its data continues to yield new discoveries.Strategy 1: Fixed Size Splitting
Technical name: Recursive Character Splitter / Fixed Token Count
How it works: Splits text every N tokens, regardless of content.
Example Output:
| Chunk | Content | Problem |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | "The Kepler space telescope was a space observatory... ## Mission Overview Kepler's sole instrument was a" | ❌ Cuts mid-sentence |
| 2 | "photometer that continually monitored the brightness... caused by planets crossing in" | ❌ Starts and ends mid-sentence |
| 3 | "front of their host star. ## Major Discoveries During its nine-year mission..." | ❌ Mixes unrelated sections |
✅ Best for: When speed matters more than quality, or you have a tight budget.
❌ Downsides: Often cuts thoughts, loses context.
💰 Cost: Low | 📈 Quality: ⭐ Low
Strategy 2: Header-Based Splitting
Technical name: Markdown Header Chunking
How it works: Looks for headings (#, ##) and keeps everything under each heading together.
Example Output:
| Chunk | Content |
|---|---|
| 1 | # The Kepler Space Telescope — "The Kepler space telescope was a space observatory... named after Johannes Kepler." |
| 2 | ## Mission Overview — "Kepler's sole instrument was a photometer... planets crossing in front of their host star." |
| 3 | ## Major Discoveries — "During its nine-year mission, Kepler observed 530,506 stars..." |
| 4 | ## End of Operations — "The mission ended in 2018 when the spacecraft ran out of fuel..." |
✅ Perfect! Each section stays intact.
❌ Limitation: Doesn't work if document has no headers (chat, emails, transcripts).
💰 Cost: Low | 📈 Quality: ⭐⭐ Medium
Strategy 3: Meaning-Based Splitting (Semantic Chunking)
Technical name: Semantic Chunking
How it works: AI measures how "similar" each sentence is to the next. When the topic changes significantly, it creates a new chunk.
Example Output:
| Chunk | Why Grouped Together |
|---|---|
| "The Kepler space telescope was a space observatory... It looked for periodic dimming, known as transits." | AI sees "telescope," "instrument," "monitor" as related concepts |
| "During its nine-year mission, Kepler observed 530,506 stars and confirmed 2,662 planets..." | Numbers and discoveries = new topic |
| "The mission ended in 2018 when the spacecraft ran out of fuel..." | "End," "deactivated" = termination topic |
✅ Benefit: Groups ideas together even if document has no headers.
❌ Downside: Slower, needs tuning.
💰 Cost: Medium | 📈 Quality: ⭐⭐⭐ High
Strategy 4: AI-Decided Splitting (Agentic/LLM-Based) ⭐
Technical name: LLM-Based Chunking / Agentic Chunking
How it works: AI reads the entire text and decides the best places to split based on logic and flow.
⚠️ Important: Why NOT to ask AI to output the full text with split markers
- 💰 Costly (duplicates all input tokens as output)
- 🐢 Slow (massive output generation)
- ❌ Hallucination risk (AI may alter the original text)
- 📏 Output token window limitations
The Correct 3-Phase Process:
PHASE 1: Pre-Split with Index Tags (No AI needed)
Split text into small fixed-size pieces (~50 tokens) and add numbered tags:
<chunk_0>The Kepler space telescope was a space observatory launched by NASA to discover Earth-size planets orbiting other stars.</chunk_0>
<chunk_1>It was named after astronomer Johannes Kepler. Kepler's sole instrument was a photometer that</chunk_1>
<chunk_2>continually monitored the brightness of approximately 150,000 main sequence stars in a fixed field of view.</chunk_2>
<chunk_3>It looked for periodic dimming, known as transits, caused by planets crossing in front of their host star.</chunk_3>
<chunk_4>During its nine-year mission, Kepler observed 530,506 stars and confirmed 2,662 planets.</chunk_4>
<chunk_5>A key finding was that 20-50% of stars visible to the naked eye likely have small, rocky planets similar in size to Earth.</chunk_5>
<chunk_6>The mission ended in 2018 when the spacecraft ran out of fuel.</chunk_6>
<chunk_7>The telescope was deactivated, but its data continues to yield new discoveries.</chunk_7>PHASE 2: AI Decision (Minimal output — just numbers!)
Ask AI: "Return ONLY the chunk indices where semantic splits should occur."
AI Response: split_after: 0, 3, 5, 7✅ AI outputs only ~10 tokens, not the entire document!
PHASE 3: Programmatic Merge (No AI needed)
Based on split_after: 0, 3, 5, 7, merge chunks:
| Final Chunk | Source | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | chunk_0 | "The Kepler space telescope was a space observatory launched by NASA..." |
| 2 | chunks 1-3 | "It was named after astronomer Johannes Kepler. Kepler's sole instrument was a photometer..." |
| 3 | chunks 4-5 | "During its nine-year mission, Kepler observed 530,506 stars and confirmed 2,662 planets..." |
| 4 | chunks 6-7 | "The mission ended in 2018 when the spacecraft ran out of fuel. The telescope was deactivated..." |
✅ Result: AI decided semantically optimal split points, original text preserved exactly, low token cost.
💰 Cost: Medium | 📈 Quality: ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Very High
Strategy 5: Summarization / Q&A Format
Technical name: Structured Output / Q&A Format / Propositional Indexing
How it works: Instead of keeping the original text, extract pure facts as question-answer pairs or structured JSON.
Example Output:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What was the Kepler Space Telescope? | A NASA observatory designed to discover Earth-size planets. |
| What instrument did Kepler use? | A photometer that monitored star brightness. |
| How many planets did Kepler confirm? | 2,662 planets. |
| How many stars did Kepler observe? | 530,506 stars. |
| Why did Kepler's mission end? | The spacecraft ran out of fuel in 2018. |
✅ Best for: FAQ systems, databases, when users ask specific questions.
❌ Downside: Loses the story and context between facts. Can hallucinate.
💰 Cost: High | 📈 Quality: ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Very High
📊 Chunking Strategies Comparison Table
| # | Strategy | Technical Name | What It Does | ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons | 💰 Cost | 📈 Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fixed Size | Recursive Character Splitter | Cuts every N tokens | Fast, simple | Cuts sentences, loses context | 💲 Low | ⭐ |
| 2 | By Headers | Markdown Header Chunking | Splits at headings #, ## | Keeps sections together | Requires structure | 💲 Low | ⭐⭐ |
| 3 | By Meaning | Semantic Chunking | AI detects topic change | Smart grouping | Slower, needs tuning | 💲💲 Medium | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 4 | AI-Decided ⭐ | LLM-Based / Agentic | AI reads and decides splits | Handles messy text | Requires AI processing | 💲💲 Medium | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 5 | Summarization | Structured Output / Q&A | Converts to Q&A pairs | Perfect for FAQ | Loses narrative | 💲💲💲 High | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
💡 Pro Tip: If AI-Decided chunking creates a chunk that exceeds your vector store's limit (e.g., 8,000 tokens), combine it with Summarization. AI decides boundaries → then oversized chunks get condensed.
Enhancing Retrieval Quality (Enhancement Strategies)
Chunking is just the beginning. Top-tier RAG systems use enhancement techniques that give each piece of text "superpowers":
Add Document Summary Context
We add global context – document title, main topic – to every chunk.
Without context (problem):
"The mission ended in 2018 when the spacecraft ran out of fuel."❌ AI doesn't know which mission!
With Document Summary:
[Source: NASA Kepler Space Telescope mission (2009-2018), exoplanet detection]
"The mission ended in 2018 when the spacecraft ran out of fuel."✅ Now a search for "fuel" or "Kepler" returns a chunk that makes sense on its own.
Search Keywords Generation
We insert likely user questions and keywords before the actual text:
kepler fuel end mission 2018 shutdown why did kepler stop | The mission ended in 2018...Enhancement Strategies Comparison
| Enhancement | What It Does | 💰 Cost | 📈 Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Document Summary | Adds context to each chunk | 💲💲 Medium | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| Search Keywords | Adds search queries | 💲💲💲 High | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Both Combined | Maximum accuracy | 💲💲💲 High | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Elite |
What Makes Data "AI-Ready"?
7 Key Properties of Quality Data

- Complete thoughts, not fragments – Text isn't cut off mid-sentence. AI gets complete information.
- Clear hierarchy – AI knows exactly where to look for answers and where supporting data is.
- Pre-prepared questions – Each block has associated questions it answers.
- Summary for each block – AI immediately understands context without reading the entire document.
- Connections between parts – Each block knows what came before. AI understands relationships.
- Metadata for filtering – Date, category, source. AI can search exactly where it needs to.
- Origin of each piece – AI can cite sources and you know it's not made up.
Example: Bad vs. Good Data
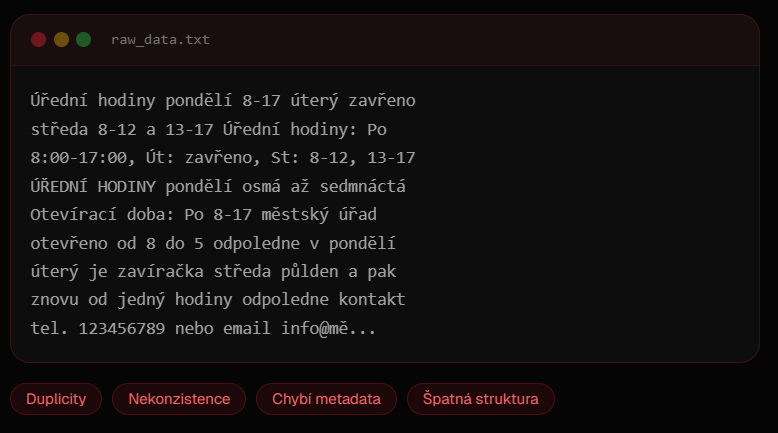
❌ Typical Reality (raw_data.txt):
Chaos. Duplicity. Missing context. AI guesses.
Office hours Monday 8-17 Tuesday closed
Wednesday 8-12 and 13-17 Office hours: Mon
8:00-17:00, Tue: closed, Wed: 8-12, 13-17
OFFICE HOURS Monday eight to seventeen
Opening hours: Mon 8-17 city office
open from 8 to 5 pm on Monday
Tuesday is closed Wednesday half day then
again from one o'clock afternoon contact
tel. 123456789 or email info@...🏷️ Problems: Duplicates | Inconsistencies | Missing metadata | Poor structure
✅ After Our Preparation (chunk_001.json):
Clean structure. Metadata. Context. AI knows.
{
// Vector searchable fields
"searchableFields": {
"rag_question": "What are the office hours of the city hall?",
"content": "Office hours: Mon 8-17, Tue closed, Wed 8-12 and 13-17",
"source_page_summary": "City Hall contact page",
"current_chunk_summary": "Office opening hours",
"overlap_summary": "...contact details and address"
},
// Filterable metadata
"metadataFields": {
"source_url": "city-hall.com/contact",
"category": "office hours",
"date_int": 20250115,
"language": "en",
"chunk_index": 3
}
}🏷️ Benefits: Optimized for RAG | Full metadata | No duplicates | Clear hierarchy
RAGus.ai: Our Solution to the Problem
What is RAGus.ai?
RAGus.ai is our specialized RAG-as-a-Service platform designed for:
- AI agencies
- Enterprise AI teams
- RAG developers
- No-code builders (Voiceflow, Botpress)
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Centralized dashboard | Manage all AI products in one place |
| Advanced analytics | Conversation stats, detailed reporting |
| Integrated helpdesk | Efficient query handling and escalation |
| Direct integration | OpenAI, Voiceflow, Pinecone, Qdrant |
| 5 chunking strategies | Including agentic (LLM) chunking |
| Fast search | Responses in milliseconds |
| Enterprise security | SOC 2, bank-grade encryption |
How RAGus.ai Solves Hallucinations
- Clean and structured data – Automatic cleaning and deduplication
- Automatic synchronization – Knowledge base is always current
- Response monitoring – Continuous improvement
- Feedback – Thumbs up/down for training
Result: 90%+ accuracy immediately, up to 99% within 3 months.
Clean and Structured Data — the Core of Successful AI
A quality AI assistant is only as good as the data you feed it. RAGus.ai is our proprietary admin panel that serves as the central brain for all your AI products. It ensures your knowledge base is always up-to-date, clear, and accurate.
Independent Knowledge Editing
Clients can improve and correct the chatbot themselves via the admin panel without any programming required.
Transcripts and Rating
Ability to browse conversation history and mark successful or unsuccessful interactions for further learning.
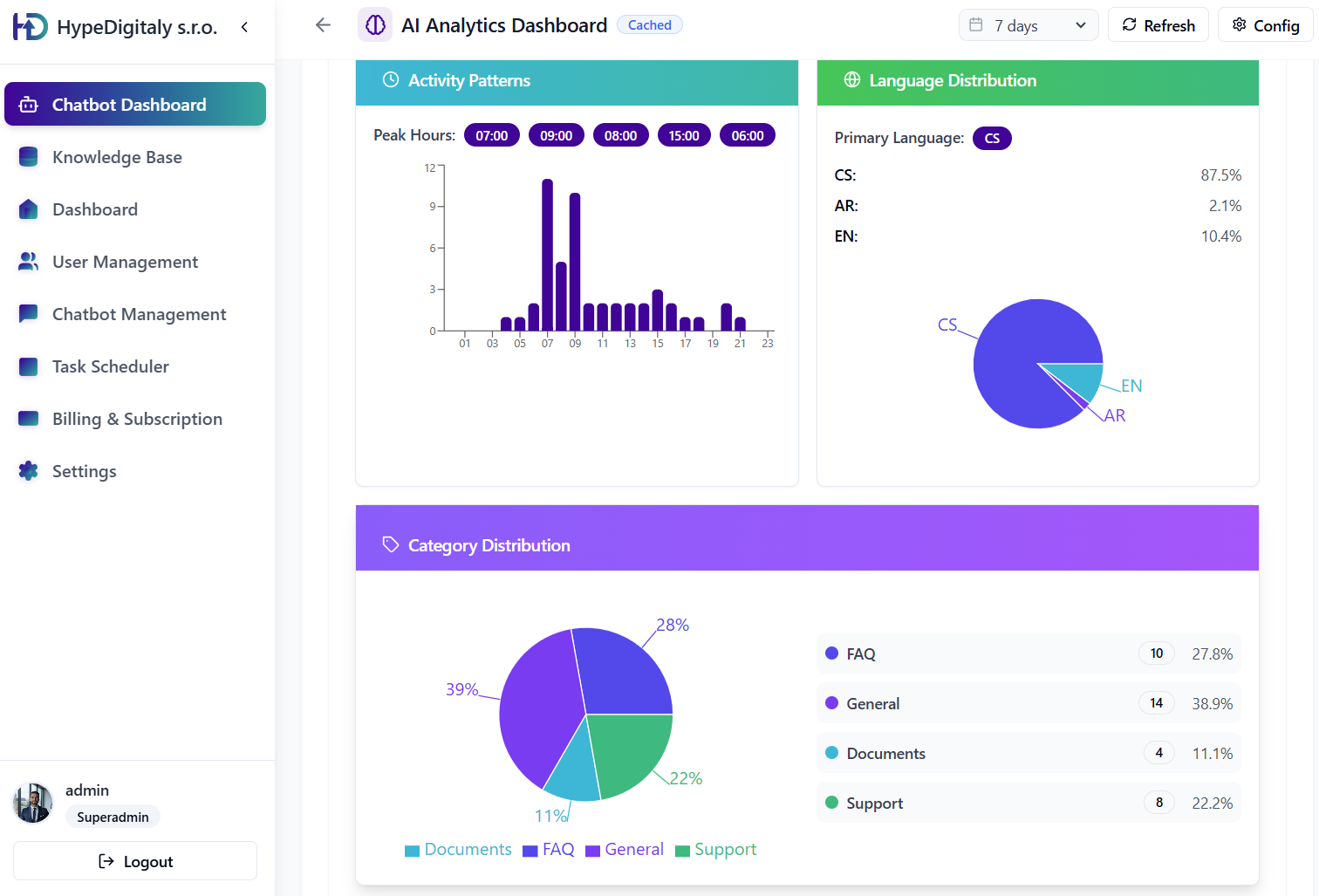
Sentiment and Trend Analysis
Categorization of most common queries and monitoring user satisfaction in real-time.
Two Paths: Service vs. Self-service
Professional Service (recommended)
For whom:
- You don't have capacity for data preparation
- You want guaranteed results without hassle
- You appreciate expert guidance and support
Price: from 2,500 CZK/hour or from 15,000 CZK per data source
👉 Order turnkey data preparation
RAGus.ai Self-service
For whom:
- You have a technical team and want control
- You need automation and scaling
- You're building your own AI products
Price: from $49.99/month
Conclusion and Next Steps
Key Takeaways
- 95% of RAG projects fail due to poor data structure
- 4 main problems: Structure, Chunking, Metadata, Updates
- 5 chunking strategies – from simple to AI-driven
- Enhancement techniques dramatically increase accuracy
- RAGus.ai offers a complete solution from preparation to monitoring
Create Your "Second Brain" for AI
It doesn't matter where your data is or what format it's in. We'll connect everything into one cohesive place – a knowledge base from which AI draws.
No searching. No guessing. No hallucinations.
*Interested in a free consultation? Contact us and we'll show you how to create one unified source of truth from scattered data.*
Want to achieve similar results?
Schedule a free consultation and discover how AI can transform your organization.
Free consultation